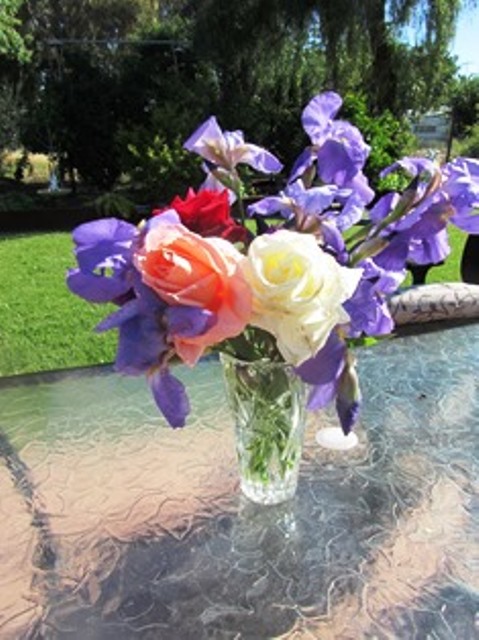
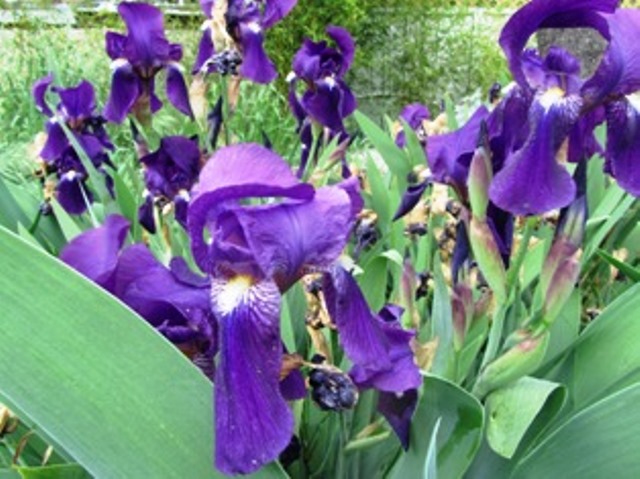
Time to Harvest Seeds from Annuals
If you are like me, you hate to see anything wasted. Case in point, seeds from a summer flower garden.
Walking around my farmette this time of year, I see many seed pods on flowers that I can take off, dry, and store. Scores of my flowering plants are perennials that come back again next year, but may others are annuals, grown throughout one season.
Just because they are annuals doesn’t mean that I have to buy new seed in order to grow them next year. No. I will gather their seeds (found in flower heads or seedpods or the calyx, located at the base of the flower on the plant). I can then pull the annual and toss the plant biomass into compost pile. The seeds I’ve collected will be further dried and stored in paper envelopes labeled with the date collected and the plant’s name and color.
In the plant store you’ll find hybridized plants along with those NOT MARKED as F1 hybrids. Seeds you collect from the non-hybridized plants will come back true to their parents the next year. Non-hybrids include heirloom, open-pollinated plants that some gardeners (myself included) prefer for their gardens.
This year, I sowed zinnia seeds that I had collected two years ago. Tossing them into a bare area of the garden, I forgot about them. When they not only grew but bloomed profusely, I felt immensely pleased with myself for taking the time to collect that seed.
Zinnias are annuals. Their tiny seeds are located in the flower heads. They can be removed once the plant has finished blooming and dried.
Nasturtiums are annuals that drop their seeds (the size of a pinto bean) and will often re-seed where they’ve grown before. I like to collect these into paper envelopes and label according to color and whether they grow as a vine or bush. They actually prefer poor soil and bloom well in full sun (less so, in shade). Nasturtiums are also edible flowers–just wash, dry, and toss into a salad or use as a garnish.
Petunias are lovely annuals that carry their seed in the calyx (just under the flower). The calyx swells with seeds so you’ll want to remove the dead flowers along with the part of the stem that includes the calyx (top of stem) . Pull off the petals. When the calyx dries and splits open, you’ll see the seeds. Save these for planting.
Marigolds add splashes of bright yellow color to your garden. Remove the dead flowers and save part of the thickened stem beneath the flower head (the calyx). Split open the calyx at the top of the stem to find the long, slender seeds. Dry and save these for your next year’s flower garden.
There are lots of other annuals that you can grow in a flower garden if you take the time to harvest and dry their seeds. Consult a gardening guide or plant grower’s catalog to learn more about the annuals you might want to grow. Then give seed harvesting a try so that you’ll get all your favorite blooms in a future garden.
____________________________________________________
If you enjoy reading about gardening and other farming topics, check out my newest novel, A HIVE OF HOMICIDES. It contains not only an entertaining mystery but also tips for growing plants and trees, keeping chickens and bees, and making delicious farm-wholesome foods.
Click here to see more: http://tinyurl.com/ya5vhhpm
The Summer Garden Is Done, What’s Next?
My summer garden is wild and chaotic and bountiful at the beginning of the season. You’ll find fruit trees, vegetables, vines of melons, corn, and perennial lavender and other showy herbs and flowers. Like a grand dame of faded elegance, the garden has matured and looks a bit weary and spent now that Labor Day approaches.
Just because the peak growing season is coming to an end, it’s not the end of garden chores. The following tasks can be started now.
HARVEST AND STORE
For some crops, the harvesting goes on. Examples include tomatoes, potatoes, melons, and winter squashes like Butternut that store well. If you haven’t already harvested the garlic, it’s a good time to do that.
Cut sunflower seed heads and place them in a warm area to dry. Collect seeds from cosmos, nasturtiums, and other flowers to preserve for next year’s garden. Work out storage options, especially for food items to be harvested.
Snip summer table grapes and other varieties if they are ripe . . . or let them hang a while longer for extra sweetness.
CLEAR BEDS
Depleted, dying, or dried annuals can be dug, pulled, and composted now. If you plan to let the garden rest, plant a cover crop so the ground doesn’t become hard scrabble. The cover crop will feed the soil.
DO FALL PLANTING
If you intend to do a fall planting, take time now to enrich the earth with amendments. Turn and rake the garden soil. Put plants directly into the prepared earth and water well to get them off to a good start.
For quick second crop before the weather turns cold, plant greens such as spinach, kale, and arugula. Cool season crops like beets, broccoli, and cabbage can go directly into the ground now, too.
CUT FLOWER AND SEED HEADS
Cut flower heads of hydrangeas for drying. Insert plant markers near peonies and other perennials that will die completely back during winter. Gather bunches of mint and other herbs, tie with string, an hang in a cool, dark place to dry.
CREATE MULCH
Designate an area to create a new compost pile. Use garden detritus and fall leaves as the trees begin to drop their canopies to enter winter dormancy. The resulting mulch will enrich the soil for next year’s garden.
CHECK ON FALL PRODUCE
Pomegranates, persimmons, and pumpkins will soon be ripening. Ensure that these plants continue to get water. Check for pests and any signs that might indicate nutrient deficiencies that could show up in the leaves. Figure out your options for storing or gifting excess fruits and veggies. For example, pomegranates keep well in the fridge or remove the seeds and put into bags for freezing. Save and dry rinds for potpourri.
TURN THE SOIL IN GROW BOXES
Aerate and amend soil in grow boxes and raised beds for cool season crops. Do these chores before the rainy season and cool weather arrives. Your garden, like a young maiden who flourishes from attention, will produce bountiful vegetables, fruits, berries, and flowers during its next growing season.
_______________________________________________________________
If you enjoy reading about farmette topics, gardening, and keeping chickens and honeybees, check out my series of cozy mysteries from Kensington Publishing in New York.
Click on this link: http://tinyurl.com/ya5vhhpm
My newest nonfiction book is published by Adams Media/Simon & Schuster: http://tinyurl.com/y9vfw2t9
- Anyone can find peace, clarity, and focus…all it takes is a moment
Seasonal Blooms for Floral Arrangements
Autumn in Northern California is one of my favorite times of the year. By November, many of the summer blooms in our flower beds have faded. Seeds have been collected for next year’s blooms. Now’s the time to put in bulbs and tubers for spring, but that doesn’t mean we have no blooms for a Thanksgiving floral arrangement.
The clocks have been turned back and the rainy season has arrived, but don’t tell that to the roses.
Red-gold roses, pyracantha berries, rustic seed pods, orange- and rust-colored zinnias, asters, willowleaf cotoneaster, and dahlias are some of the garden plants that combine beautifully in a fall floral arrangement. To the harvest table, I also like to add some seasonal fruits like pomegranates and persimmons.
Thanks to the recent rain, the bougainvillea blazes in shades of fuchsia, orange, red, and purple. Zinnia’s near the farmette’s bee house are still holding color and hanging on until cold weather arrives.
And while pyracantha (fire thorn) berries add splashes of bright orange to a dark corner of the garden where bamboo towers to ten feet, the Chinese lantern plant holds aloft dozens of small pink blooms like little lanterns.
With Thanksgiving three weeks away, I’m feeling confident that our table arrangement will include some of the season’s festive berries, seed pods, and blooming flowers collected from around the farmette.
In the meantime, I’ll notice the splashes of color to be discovered here and there and consider how to use them in a holiday bouquet.
* * *
NEWLY RELEASED–The Murder of a Queen Bee (Kensington Publishing, NY–Sept. 2016).
Discover delicious farm-to-table recipes, farming tips, and wisdom as well as sort out a charming whodunnit. Also, enjoy gardening tips and farm sayings. Dig for clues while learning about bees and chickens. To learn more, click on the link under the picture.
See, http://tinyurl.com/h4kou4g
See, http://tinyurl.com/hxy3s8q
This debut novel launched the Henny Penny Farmette series of mysteries and sold out its first press run. It’s now available in mass market paperback and other formats.
Gathering Seed for Next Year’s Garden
The sounds of summer around our farmette have grown quieter. It’s mid-August and the neighborhood children have returned to school. I miss their laughter. I miss the delight on their faces at seeing the chickens and the honeybees. I miss keeping them company at their lemonade stand.
But I admit to the secret pleasure of solitude and quiet, though it isn’t really silence. It’s the peaceful clucking of chickens and the twitter of songbirds as I gather seed from plants that have bloomed and dried, such as the cosmos, nasturtiums, sunflowers, and wisteria.
The wisteria vine that exploded in growth of long, green tendrils during spring and early summer and graced us with bracts of purple perfusion now hold heavy pods. The pods contain seeds that can be dried and planted for new vines next year.
The sword-shaped leaves of the irises are dry–their blooms a memory from early spring. I’ve already cut their long leaves back into four-inch fans and will dig some of the rhizomes for replanting in other beds around the farmette.
The sunflowers that the bees love to forage on have gone to seed. Those seeds will become next year’s plants, but some we’ll save for the squirrels.
The red and yellow onions have developed seed pods on long shoots now. I’ll plant those in raised beds in the fall for a spring crop of onions.
Yes, the dog days of summer have come around again. But the growing season continues. End of summer gives rise to autumn when grapes, persimmons, pumpkins, figs, and pomegranates ripen. On the farmette, there is always another season and other crops to look forward to with anticipation. It’s the good life.
Backyard Gardeners and Farmers Have a Choice
We gardeners and farmers have a choice when putting in our gardens, fields, and orchards. We can choose open-pollinated, heirloom seeds, hybrids seeds, or GMO seeds. I much prefer the old-fashioned way of seed-saving and sharing of open-pollinated, heirloom varieties.
On our farmette, we routinely save seed from plants we grow in one season and use them during another. We have picked apricots from our backyard trees, saved the seeds, and grown new trees that (this year) bore fruit.
We’ve exchanged seeds with our neighbors who also keep organic gardens and prefer open-pollinated seeds. Seeds that are hybrid and/or GMO usually are patented, meaning scientific companies or growers own those patents.
Open-pollinated seeds do not carry patents and remain available to all of us to plant and replant.
Gathering seeds from the plants one grows is how our grandparents did it. I go around plucking seed heads from cosmos, purple cone flower, and the hardened seeds of nasturtiums when the flowers have faded. I’ve taken cuttings of all my roses and have been given clips from friends and neighbor’s bushes and now plenty of roses to line walkways and fill a garden.
This year, an apricot tree that we started two years ago after we ate the fruit and planted its seed, bore beautiful cots that I turned into jam. I’ve got a bountiful crop of onions (red and yellow) and garlic and peppers this year from last year’s seed. The cycle goes on.
The acronym GMO stands for “genetically modified organism.” The phrase means that scientists have used recombinant DNA technology to create the seed. In some cases, the purpose is to create seeds with pesticides spliced into their DNA to repel pests.
Some gardeners see this process by chemists, scientists, and researchers working of large petro-chemical companies as a dangerous venture into biological processes that have a long evolutionary history. Further, the concern encompasses the potential negative ramifications of genetically engineering a plant–what farmer wants to handle seed (much less eat the plant) that has warning labels about pesticides integrated into the seeds?
If gardeners stick with open-pollinated seeds and participate in seed saving and sharing, together we can ensure our Earth’s biodiversity continues. The other prospect is scary. Many species and cultivars of plants are no longer available. They are no longer being grown. Some have become extinct.
What Could Be Easier than Growing Irises in Raised Beds?
When we first moved to the Bay Area from Miami, the heirs to the property behind ours gave us some bearded irises that had been planted in the 1950s by their parents. I recall the beauty of irises on my grandmother’s farm in Missouri. She called them flags.

For a lovely raised flower bed, plant other bloomers like cosmos, geraniums, pansies, nasturtiums, and marigolds with iris cultivars
Mostly colored in deep purples and blues, white, and pinkish-beige, the bearded irises have added an aesthetic appeal to our farmette that was mostly just a big field with a tiny house in the middle. We’ve planted them in the ground, along fences, and in raised boxes.
Easy to grow and maintain, the irises have become one of our favorite flowers. We’ve kept them going in our garden and they’ve rewarded us with many new rhizomes.
As we’ve continued to restore the farmette, we’ve built many four by six feet boxes for raised beds. The materials cost roughly $125 per box. We like them because we can easily control the soil (building it up with compost, manure, and other amendments), drainage, tilling, and weeds. Recently we decided to make irises the mainstay of a raised bed border.

We’ve interplanted citrus and bearded irises in this raised bed spanning the length of the front fence
Over the weekend, we built a long raised bed that extends the entire length of the fencing on the southwestern side of our property. In it, we planted lots of citrus trees, climbing roses, and irises. If you are thinking of doing something comparable, have fun choosing from among the hundreds of cultivars of bearded and Siberian irises.
Plant them about three inches deep and a few inches apart in well drained, fertile soil. Irises need shade from the hottest sun and enjoy a deep drink of water, especially during blooming. I enjoy the ease of growing them in raised beds and love, love, love the magnificent color atop tall stalks when they bloom.
 Facebook
Facebook Goodreads
Goodreads LinkedIn
LinkedIn Meera Lester
Meera Lester Twitter
Twitter